This blog is based on the fact sheet on Actionable Guidance for Local Governments: Harnessing Water Point Data for Improved Water Services
Local governments use water point data to determine the status of water services, make district investment plans, support communities, and advocate for district programs. They are a tool for guiding and coordinating partners working in an area and acquiring the financing required for sustainable water services. Local governments may work with partners to overcome barriers such as inadequate human resources and logistics for data collection and analysis.
Previously, we wrote blogs about universal lessons for improving water point monitoring and guidance for national governments. This blog highlights the most important lessons for local governments. The recommendations for local government apply equally to other service authorities involved in planning, coordination, regulation, and oversight of water services and technical assistance to water service providers and communities.
Recommendation 1: Require the use of national and district standards to monitor results
Require NGOs and the private sector to collect water point data meeting national standards, to monitor results, and to share their data with the district and other stakeholders. They should have to explain the results of their water point monitoring during coordination meetings. Provide feedback to the national government when there are challenges using data.
Recommendation 2: Use water point data to tell the story of water services
Use water point data to tell the story of water services to politicians, financiers, and users to sustain interest in achieving universal access to basic water services. Evidence-based investment plans using water point data can facilitate dialogue between water engineers, planners, and politicians on how to improve services.
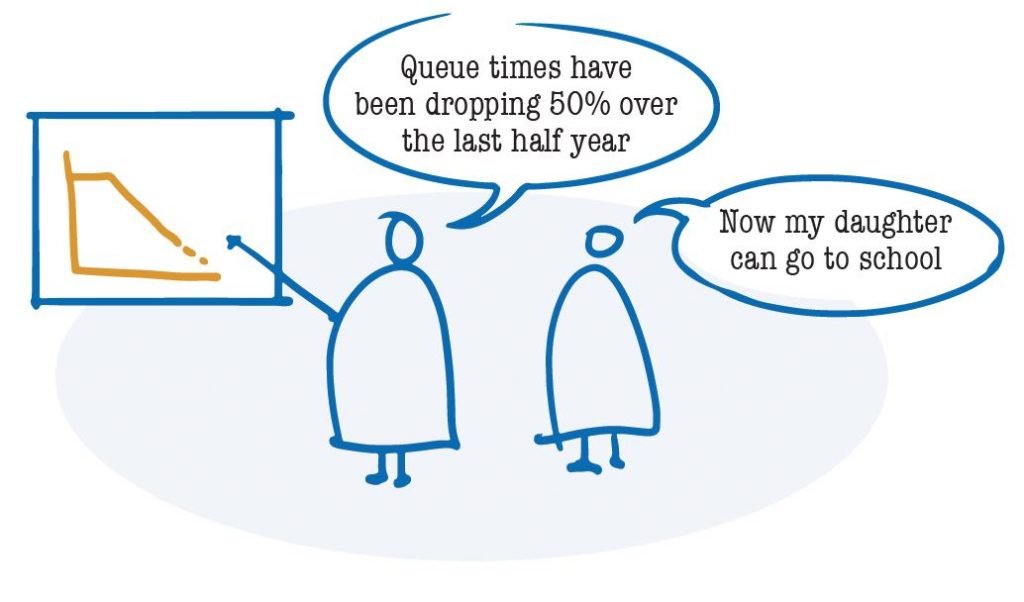
Coordination and advocacy in Kamwenge, Uganda
In Kamwenge, water point data are used in coordination meetings at the district level. The use of water point data has facilitated the distribution of resources, identification of infrastructure failure rates, and development of the District Investment Plan in 2015. The investment plan estimates what financial resources are needed to reach everyone by 2030. This has enhanced active participation of local politicians using functionality and coverage data to advocate for water services.
Recommendation 3: Use water point data to plan and design with partners
Use water point data to plan corrective actions and design programs with partners. For this to work efficiently, development partners and government must work with the same standards and indicators. Ensure local lessons are included in the choice of data to collect.
National monitoring data used in 11 districts in Ghana
After the publication of the national “Framework for Assessing and Monitoring Rural and Small Town Water Supply Services in Ghana”, monitoring data have been used in 11 districts to inform District Water and Sanitation Plans. It has informed repairs and rehabilitation of over 600 boreholes with hand pumps restoring water services to an estimated 180,000 people and has stimulated several local governments to form or reconstitute the teams managing water points under two donor-funded programs.
Reference
The White Paper “Harnessing Water Point Data” presents the details of what water point data are, how they are used, and how they can be used more effectively to measure services and water resources, strengthen the enabling environment, and improve coordination. It also discusses the impact of recent innovations such as the remote monitoring of water points using mobile technology.
The White Paper can be downloaded here: Harnessing Water Point Data to Improve Drinking Water Services